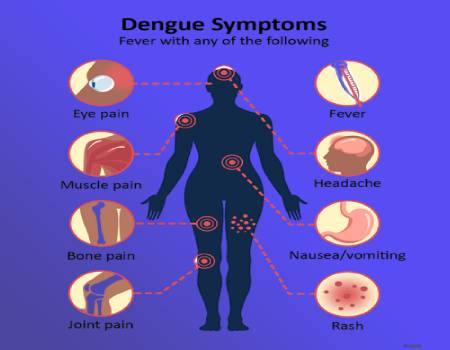
- High fever
- Severe headache
- Pain behind the eyes
- Joint and muscle pain
- Skin rash
- Mild bleeding, such as nosebleeds or gum bleeding
- Fatigue
Severe Dengue: In some cases, dengue fever can progress to severe dengue, also known as dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome. Severe dengue symptoms include:
· Severe abdominal pain
· Persistent vomiting
· Bleeding from the nose or gums
· Difficulty breathing
· Fluid accumulation in the abdomen or chest
· Organ damage
· Severe dengue is a medical emergency and requires immediate hospitalization.
Prevention of Dengue Fever:
Preventing dengue fever primarily involves reducing the risk of mosquito bites and eliminating mosquito breeding sites. Here are some preventive measures:
Use Mosquito Repellent: Apply mosquito repellent on exposed skin and clothing, especially during peak mosquito activity times.
Wear Protective Clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants to reduce skin exposure.
Install Window and Door Screens: Ensure that doors and windows have screens to keep mosquitoes out.
Eliminate Mosquito Breeding Sites: Mosquitoes that carry the dengue virus breed in standing water. Empty, cover, or treat containers that collect water, such as flower pots, buckets, and water storage tanks.
Community Efforts: Encourage your community to participate in mosquito control activities, such as removing stagnant water and keeping the environment clean.
Stay Indoors: During peak mosquito activity times, stay indoors or use mosquito nets if sleeping outdoors.
Treatment of Dengue Fever:
There is no specific antiviral medication for dengue fever, so treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. If you suspect you have dengue fever, it's essential to seek medical attention, especially if you experience severe symptoms.
Fluid Replacement: Adequate hydration is crucial. In mild cases, drinking oral rehydration solutions can help. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for intravenous fluid replacement.
Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, like acetaminophen, can help reduce fever and alleviate pain. Avoid non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, as they can increase the risk of bleeding.
Monitoring: Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals is essential to detect any signs of severe dengue early.
Blood Transfusion: In cases of severe dengue with significant bleeding or low platelet counts, blood transfusions may be required.
Rest: Getting plenty of rest is important to support the body's recovery.
In conclusion, dengue fever is a viral disease transmitted by mosquitoes and can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe. Prevention is key, and measures to reduce mosquito exposure and breeding sites can significantly reduce the risk of infection. If you or someone you know shows symptoms of dengue fever, seek medical attention promptly to ensure proper care and management of the illness. Dengue fever is a serious health concern, especially in regions where it is endemic, and public health efforts are ongoing to control its spread and reduce its impact on affected communities.